Chmod Linux Permissions Chart
Rwxr-xr-x My understanding is that you have a 9 bit permission Changing permissions with chmod (numbers) Download your favorite Linux distribution at LQ ISO.

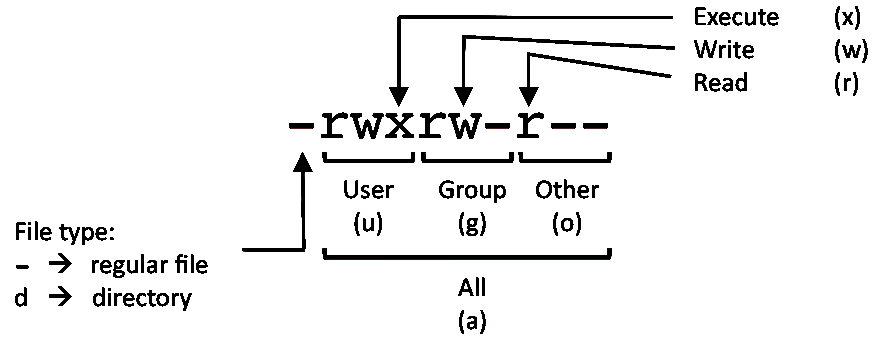
Chmod linux permissions chart. A chmod command first appeared in AT&T Unix version 1. You are giving read, write and execute permission to the owner user but the groups members and others have no permissions at all. Read (`r'), write (`w'), and execute (`x').
The Linux command to change permissions on a file or directory is chmod, which we like to read as change file mode. I’ll also explain some the popular terms like chmod 777 or chmod 755 or chmod -r. Use the following procedure to change permissions in symbolic mode.
If you need to list a file's permissions, use the ls command. Group can read only;. Hi, I am unsure how the following command #chmod 755 file, results in the permission:.
Only the current owner or superuser can use the chmod command to change file permissions on a file or directory. A file’s permission is changed by root or the owner of the file. Rwxrwxrwx ) to see its value in other formats.
The chmod system call cannot change their permissions. CHMOD is used to change permissions of a file. The chmod command changes the access permissions of files and folders.
One set for the owner of the file, another set for the members of the file’s group, and a final set for everyone else. User can read, write, and execute;. Take a new file's group from parent directory, as described in chown(2) and mkdir(2)).
Chmod 300 (chmod a+rwx,u-r,g-rwx,o-rwx) sets permissions so that, (U)ser / owner can't read, can write and can execute. The name speaks for itself. To meet our goal, we will run:.
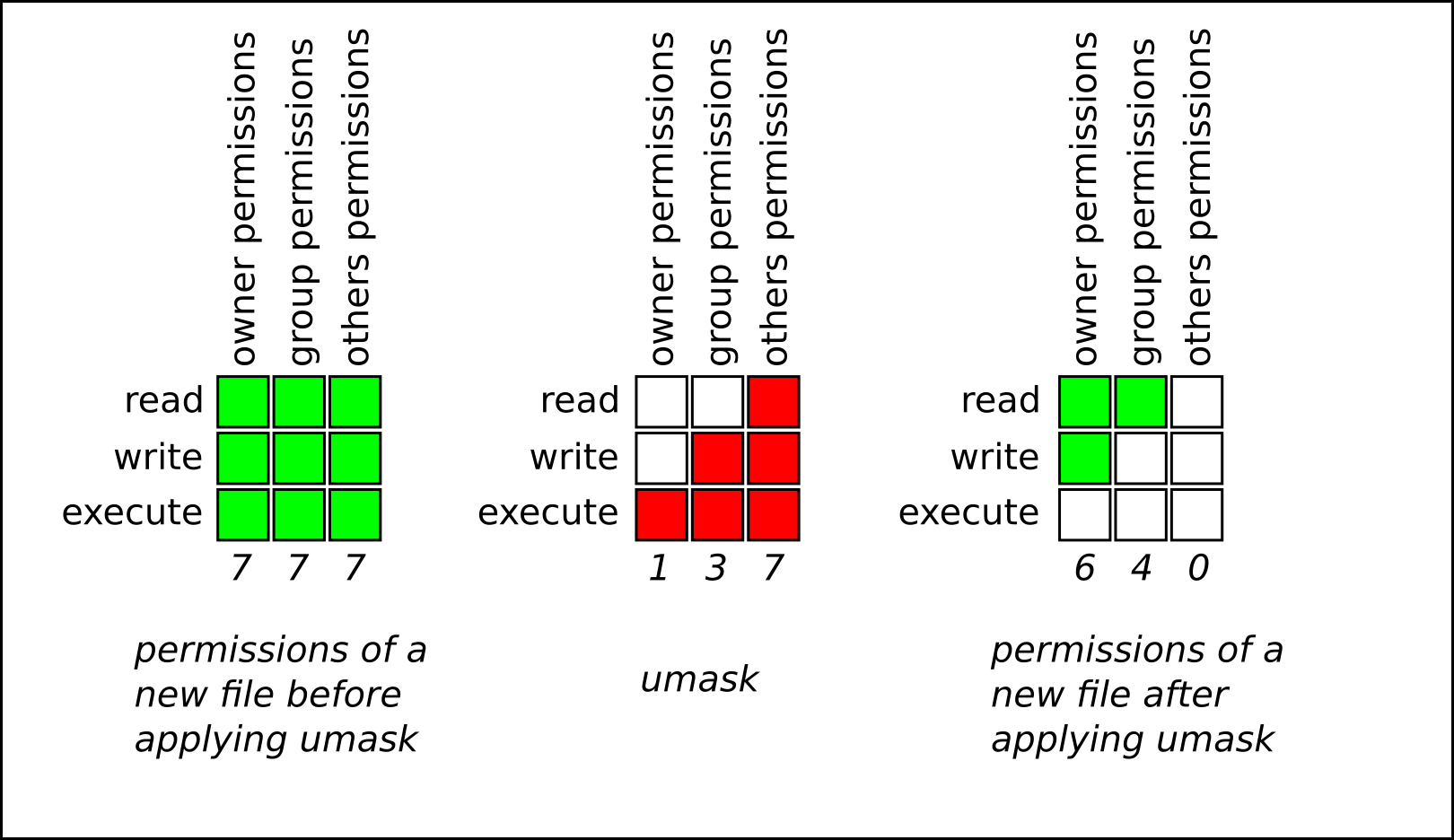
The chmod command is used to alter the permissions of a file. If you are not the owner of the file or directory, become superuser. If the mask has a bit set to "1", it means the corresponding initial file permission will be disabled.A bit set to "0" in the mask means that the corresponding.
777 ) or symbolic notation (e.g. It’s usually used when installing and configuring various services and features in a Linux system. Chmod.(change mode) is a widely used command to change the permissions of files and directories.It allows the setting of user, group and other bits which each define what rights each classification of user has over the files.
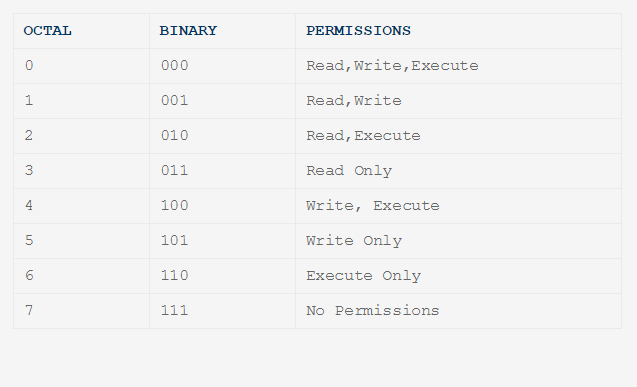
This tutorial explains chmod command symbolic notation (r, w, x, a) and octal notation (0, 1, 2, 4) in detail with chmod command arguments and options. Users can simply modify file permissions using the chmod (change mode) command. The table below gives numbers for all permission types of a File/Directory.
Obviously, there's a need to keep things organized and secure. For example, to change the permissions of all files and subdirectories under the /var/www/html directory to 755 you would use:. This permission give you the authority to open and read a file.
As systems grew in number and types of users, access control lists were added to many file systems in addition to these most basic modes to increase flexibility. It may be used to add or remove permissions. Rwxrwx--- How does 770 correspond to rwxrwx---?.
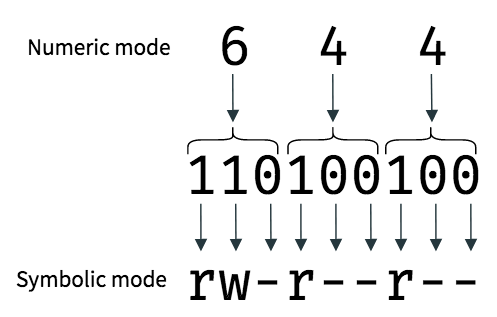
Recursively (-R) Change the permissions of the directory myfiles, and all folders and files it contains, to mode 755:. Permissions are a bit mask, for example, rwxrwx---is in binary, and it's very easy to group bits by 3 to convert to the octal, than calculate the decimal representation. Set the permissions of file.htm to "owner can read and write;.
/home/user> ls -l foo-rwx--x--- 1 user user 78 Aug 14 13:08 foo /home/user> chmod go+r foo /home/user> ls -l foo-rwxr-xr-- 1. Chmod is a command in Linux and other Unix-like operating systems that allows to change the permissions (or access mode) of a file or directory. Chmod -R 755 myfiles.
Chmod o+t ~/Desktop/test or. Linux chmod command is one of the most commonly used commands especially by system administrators when assigning modifying file and folder permissions. In this guide, you will learn about the chmod command.
How to Change Permissions in Symbolic Mode. Chmod never changes the permissions of symbolic links;. The command can accept one or more files and/or directories separated by space as arguments.
How To Change File Permissions In Linux Using ‘chmod’ Command. To change the permissions — or access mode — of a file, use the chmod command in a terminal. (G)roup can't read, can't write and can't execute.
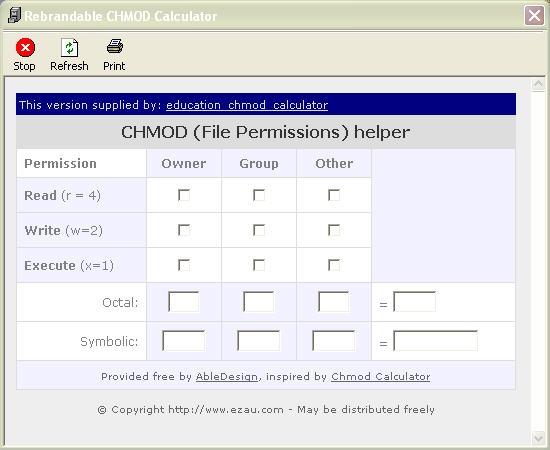
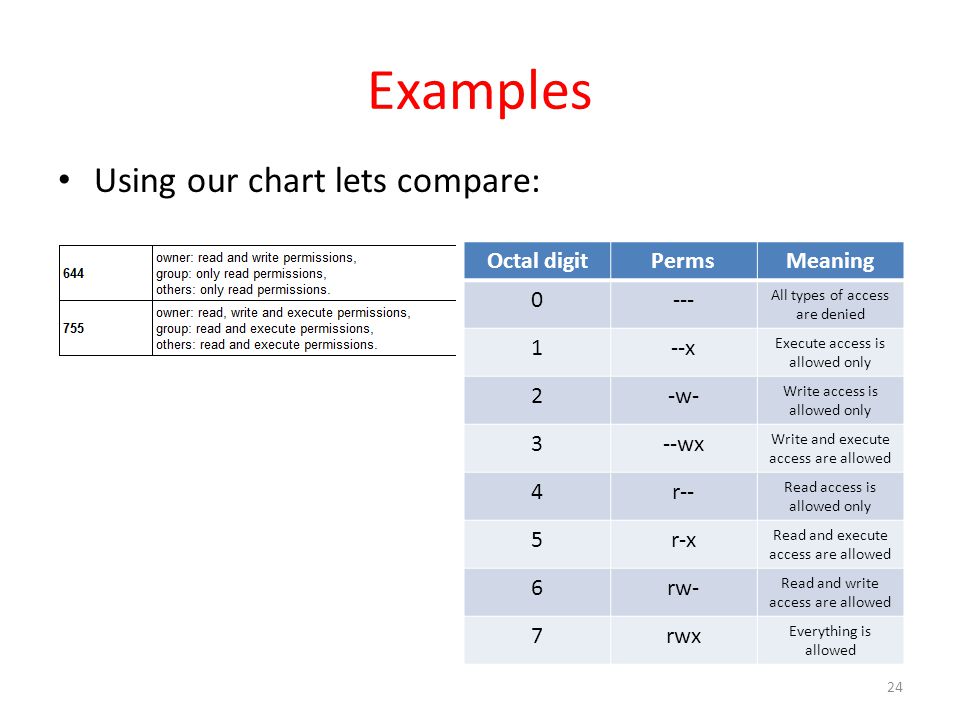
Chmod Calculator is a free utility to calculate the numeric (octal) or symbolic value for a set of file or folder permissions in Linux servers. The tool will provide you with an octal code that corresponds to these permissions which can then be applied to relevant directories and files with chmod. 777 = rwxrwxrwx 755 = rwxr-xr-x 644 = rw-r--r-- 700 = rwx------ 750 = rwxr-x---.
In Linux, who can do what to a file or directory is controlled through sets of permissions. Chmod -R 755 /var/www/html. Each permission may be `on' or `off' for each of three categories of users:.
Others can read only". Chmod is a Linux command that will let you "set permissions" (aka, assign who can read/write/execute) on a file. If we want to change the permission of a file for a group of users then a command called chmod is used to do this.
755, etc.) What am I to type in terminal to know the chmod of the file or folder I want?. The chmod command has also been ported to the IBM i operating system. And the last number represents the permissions for all other.
(O)thers can't read, can't write and can't execute. Also, generates the corresponding unix command. Now each of these categories (User/Group/Others) can have combination of Read, Write or Execute permissions.
Octal 2 means to set group ID on the file. The chmod command, like other commands, can be executed from the command line or through a script file. Umask or file mode creation mask is a grouping of bits, each of which restricts how its corresponding permission is set for newly created files or directories.
Chmod is a UNIX and Linux command for setting file or directory permissions. Here is a short note/cheat sheet for Linux directory and file permissions. This is basically because it was conceived as a networked system where different people would be using a variety of programs, files, etc.
To change permission using the Linux chmod command we have to follow some syntax and rules. There are three sets of permissions. The chmod command allows you to change the permissions on a file using either a symbolic or numeric mode or a reference file.
Chmod +t ~/Desktop/test Numerical/octal way (1, sticky bit bit as value 1 in the first position) chmod 1757 ~/Desktop/test Now let us test the results:. And you need an octal to change file mode. Changing User File and Group Ownership Aside from changing file permissions, you may come across a situation that requires changing the user file ownership or even group ownership.
How to use Check the desired boxes or directly enter a valid numeric value (e.g. The first number represents the Owner permission;. The syntax is as follows:.
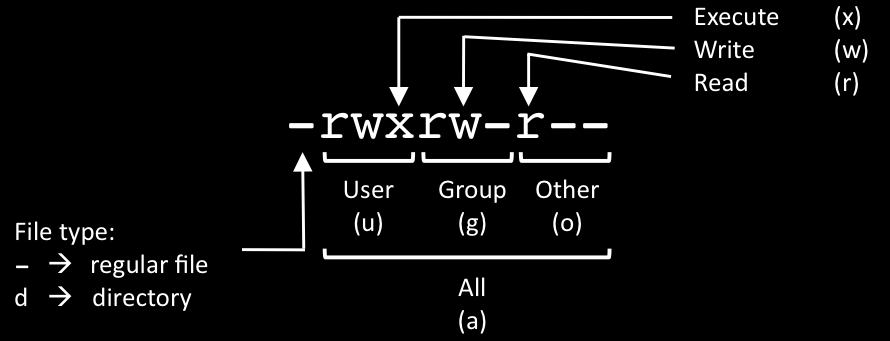
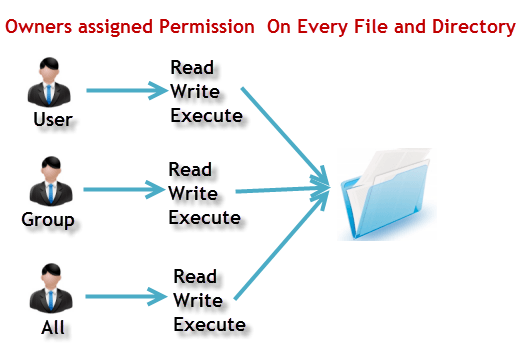
Other people in the same group as the owner;. The second represents the Group permissions;. There are three specific UNIX/Linux file system permissions - read (r), write (w), and execute (x).Permissions are grouped into three sets or triads, each defining access for different scope or class:.
Chmod 2770 Chmod 2770 (chmod a+rwx,o-rwx,ug+s,+t,u-s,-t) sets permissions so that, (U)ser / owner can read, can write and can execute. The first octal digit sets the setuid, setgid and sticky bits (see this article for more details on setuid/setgid). The permissions control the actions that can be performed on the file or directory.
User Group Other Read 4 4 4 Write 2 2 2 Execute 1 1 1 U G O X X X Chmods:. Chmod permissions file OR:. Chmod permission1_permission2_permission3 file When using chmod, you need to be aware that there are three types of Linux users that.
Read - 4 Write -2 Execute - 1 So if a file has read,write, execute permissions for User and read,execute permission for Group and Others both then it is denoted as chmod 755 filename also, chmod u+rwx, g+rx, o+rx filename. The letter or letters representing the owner (u), group (g), other (o) or all (a) followed by a + for adding permissions or a – for taking away permissions and then the letter for the permission (r for read, w for write and x for execute).In the above example, I added the execute permission for all users. S_ISUID () set-user-ID (set process effective user ID on execve(2)) S_ISGID (000) set-group-ID (set process effective group ID on execve(2);.
Examples chmod 644 file.htm. Chmod Modifies File Permissions. Chmod a+X * gives all users permission to execute files (or search directories) if anyone could before.
PERMISSION COMMAND U G W rwx rwx rwx chmod 777 filename rwx rwx r-x chmod 775 filename rwx r-x r-x chmod 755 filename rw- rw- r-- chmod 664 filename rw- r-- r-- chmod 644 filename U = User G = Group W = World r = Readable w = writable x = executable - = no permission. The new file mode is specified in mode, which is a bit mask created by ORing together zero or more of the following:. Select the permissions you require below.
Ls -li ~/Desktop/test drwxrwxrwt 45 hadi hadi 485 Mar 11 14:35 ~/Desktop/test To delete/Remove a sticky bit. Converts from octal notation to rwx notation or symbolic mode and vice-versa. With this, you are giving read and write permission to the owner user.
Linux File/Directory Permissions cheat sheet. It is a confusing topic until you learn it, but it is needed if you plan to work with UNIX or Linux web servers. Below is the command's general structure:.
The three user levels are Owner, Group, and Other. Group members and others cannot read, write or execute. (G)roup can read, can write and can execute.
How to Set File Permissions Using `chmod' Files and directories in Unix may have three types of permissions:. Group – The Group permissions apply only to the group that has been assigned to the file or directory, they will not effect the actions of other users. Leading 0 means this is octal constant, not the decimal one.
A sample permission string would be chmod 640 file1, which means that the owner has read and write permissions, the group has read permissions, and all other user have no rights to the file. Permission can be changed by the binary equivalent of the permission added. Linux File Permission Commands Change permission for a file.
So, the equivalent would be to do a chmod a+rwx filename, then chmod g+s filename.The chmod info page does explain this in more detail. The mode can also be specified using the symbolic method:. The highly productive Linux system offers various levels of permission to ensure that the user has enough ways to interact with files and directories.
Let us understand the Permission system on Linux. Group members and other users can read and execute, but cannot write. Linux has inherited from UNIX the concept of ownerships and permissions for files.
We will explain the modes in more detail later in this article. Before you see the chmod examples, I would strongly advise you to learn the basics of file permissions in Linux. Every file and directory in your UNIX/Linux system has following 3 permissions defined for all the 3 owners discussed above.
0644 (octal) is 0.110.100.100 in binary (i've added dots for readability), or, as you may calculate, 4 in. Please note that chmod 777 filename is the equivalent of chmod 0777 filename in this example. If you need a more in-depth guide on how to use Chmod In Linux to change file permissions recursively, read our Chmod Recursive guide.
CHMOD Permissions Reference Chart by David · September 18, 12 This is how I remember permissions and most likely, it will help you remember it as well. 400 read by owner 040 read by group 004 read by anybody (other) 0 write by owner 0 write by group 002 write by anybody 100 execute by owner 010 execute by group 001 execute by anybody So to manually set permissions, simply add up the columns. The chmod command can be used with either a text-based argument or 3 octal digits (see note 1) to change the permissions on a file.An example of the text-based command to add "read" permission for group members and others to a file named foo is:.
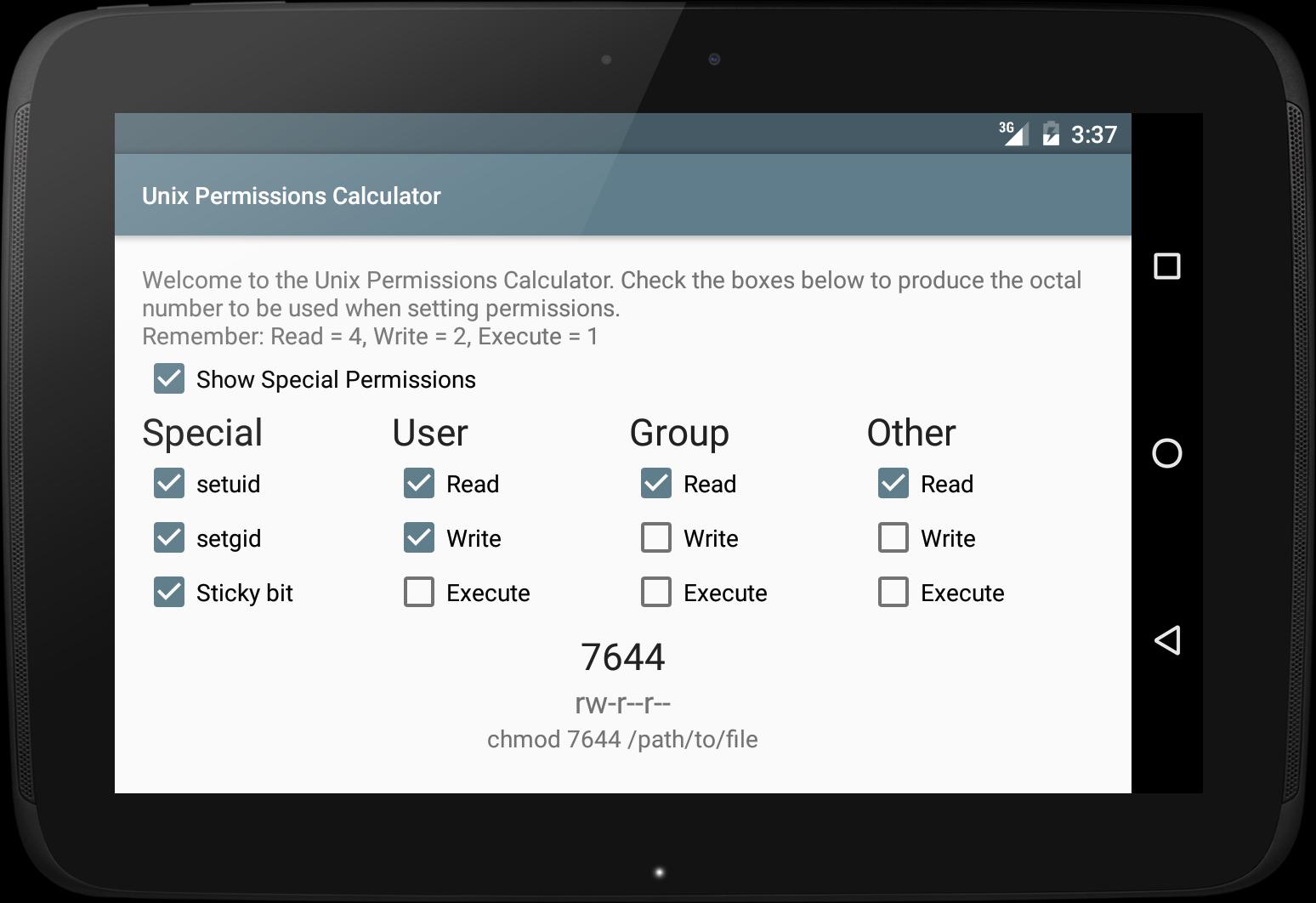
Chmod is used to make changes:. Running chmod 770 on project-a gives us the permission set we want:. Online Unix or Linux file / directory permissions calculator.
Anybody can read, write, execute. Read permission on a directory gives you the ability to lists its content. Using chmod command will be a lot easier once you understand the permissions.
The file or directory owner;. Even the owner cannot execute the file with this permission set. Chmod o-t ~/Desktop/test Now let us test the.
Additionally server-side languages provide functions that are roughly analogous to chmod in terms of operation using absolute notation. Set the permissions for a file or directory by using the chmod command. Change permissions in symbolic mode by using the.
Each of the three digits in our chmod statement — 7, 7, 0 — corresponds to Owner, Group, and Others rights. This works in any linux distro, such as Ubuntu, etc. I can look in properties of this folder but I want to get properties fast and in digits (octal, e.g.
Chmod has two operating modes:. Each file and directory has three user based permission groups:. Each row has 2 examples, one for setting that permission for a file, and one for a directory named ‘dir’.
Unix Permissions / chmod Calculator. The exact command is. User/owner (u), group (g), and everyone else/others (o).Permissions can be presented either in numeric (octal) or symbolic notations.
Owner – The Owner permissions apply only the owner of the file or directory, they will not impact the actions of other users.;. Linux Chmod Permissions Cheat Sheet. Mandatory locking, as described in fcntl(2);.
Here is a chart of the permissions displayed by ls and the corresponding octal values:. Learn how chmod command is used to manage Linux permission levels (user, group and other) and types (read, write and execute) step by step with practical examples. There are three different possible user levels, each with three different possible settings.
The version of chmod bundled in GNU coreutils was written by David MacKenzie and Jim Meyering.

An Introduction To Linux Permissions Digitalocean

Chmod Calculator The New Trend Convert For Free

Images ged With Chmod On Instagram
Chmod Linux Permissions Chart のギャラリー
Chapter 5 Managing File Permissions Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8 Red Hat Customer Portal
Online Chmod Calculator Free Easy To Use Converter What Is Chmod Calculator Convertforfree Wattpad
.png)
File Permissions In Linux Unix With Example

Change File Permissions Easily With Online Chmod Calculator By Chmodcalcu Issuu
How To Change Permissions Chmod Of A File Hostgator Support

Tweaking4all Com Chmod Calculator Set File Permission With Chmod
How To Change Permissions Chmod Of A File Hostgator Support

File Permissions Operating Systems I Ppt Download

Linux Admin 101 File Permissions With Chmod Chgrp And Chown Trash Computer

19b Permissions

Chmod 777 755 655 644 And More Permissions Linux Files Tutorials
.png)
File Permissions In Linux Unix With Example
Education Chmod Calculator Standaloneinstaller Com

Chmod 777 755 655 644 And More Permissions Linux Files Tutorials

File Permissions In Linuxunix With Example Linux Lab 05 Unix And Linux File Permissions

An Introduction To Linux File Permissions Boolean World

Chmod 777 755 655 644 And More Permissions Linux Files Tutorials

19b Permissions
Workbook 4 File Ownerships And Permissions Ppt Video Online Download

Chmod Unix Permissions Chmod Calculator Chmod Generator Softaox

Linux Admin 101 File Permissions With Chmod Chgrp And Chown Trash Computer

Unix Permissions
Verizon Droid Turbo Has Been Rooted Page 2 Droidforums Net Android Forums News

19b Permissions

How To Use File Permissions In Linux 9 Steps With Pictures

19b Permissions
Chmod Directory Read Write And Type

Unix Chmod Cheat Sheet Computer Science Programming Learn Javascript Linux Operating System

An Introduction To Linux Permissions Digitalocean

Chmod Umask Stat Fileperms And File Permissions
Unix Linux Permissions Calculator For Android Apk Download

Is There A Web Based Converter Between Rwx And The Octal Version Unix Linux Stack Exchange

Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks
Q Tbn 3aand9gcsacd7mr Ecztzl Lq8wap9enfi2vj2xlffbqx6amvc25tn3 R6 Usqp Cau
Chmod Cheat Sheet Dan Flood

Your Own Linux Chmod Basics Of Files Directories Permissions And Use Of Chmod

Change File Permissions Easily With Online Chmod Calculator Convert

Reliable Online Converter Online Calculator Online Converter Coding

Understanding Basic File Permissions And Ownership In Linux The Geek Diary

Chmod Calculator Chmod Generator Chmod Command

What Is Chmod And Chmod Calculator Convert For Free

File Security
Rainsserver Chmod Command

Chmod File Permissions In Linux Unix

Give Write Access Chmod

Chmod Wikipedia
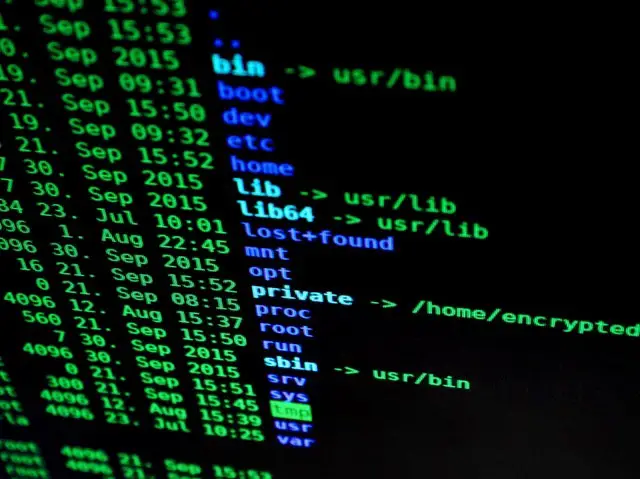
An Introduction To Linux File Permissions Boolean World

Linux Permissions Deep Dive Part 1 By Runcy Oommen Medium

Unix Linux Permissions Calculator For Android Free Download And Software Reviews Cnet Download Com

19b Permissions

Chmod Permissions Reference Chart David Biers

Chmod Write Access

Understanding File Permissions

Everything About Chmod Command In Linux Hackerearth

Chmod 777 755 655 644 And More Permissions Linux Files Tutorials

Is There A Web Based Converter Between Rwx And The Octal Version Unix Linux Stack Exchange

19b Permissions

Linux File Permissions And Chmod Doug Vitale Tech Blog

A Unix And Linux Permissions Primer Daniel Miessler
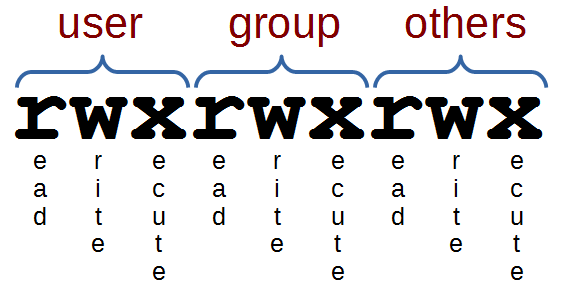
Read Just Enough Linux Leanpub

Project Ii Six Task Management System Linux File Permissions Programmer Sought

An Introduction To Linux File Permissions Boolean World

Setting File And Directory Permissions Computational And Information Systems Laboratory

Online Chmod Calculator Free Easy To Use Converter What Is Chmod Calculator Convertforfree Wattpad

Os Mkdir And Os Mkdirall Permission Value Stack Overflow
Q Tbn 3aand9gctejwme2dmdomohoy140oy72qp3e1pn8jtuanchtus Usqp Cau

Project Ii Six Task Management System Linux File Permissions Programmer Sought
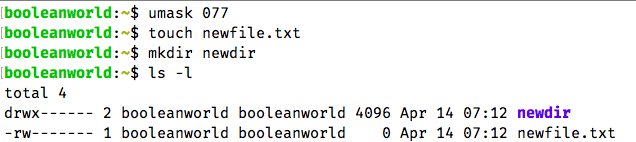
An Introduction To Linux File Permissions Boolean World

Execute Vs Read Bit How Do Directory Permissions In Linux Work Unix Linux Stack Exchange
Q Tbn 3aand9gctffpe8 Toaseevlghfe6e9aybdh2x Q9ffbgxz8vseo1oxnuzl Usqp Cau

Change File Permissions Easily With Online Chmod Calculator Convert

Opensuse News
Q Tbn 3aand9gctcuilq Yqqxkzwxdz3pdmp0f Jyy70pg6dtr6qeavirn8zjzor Usqp Cau
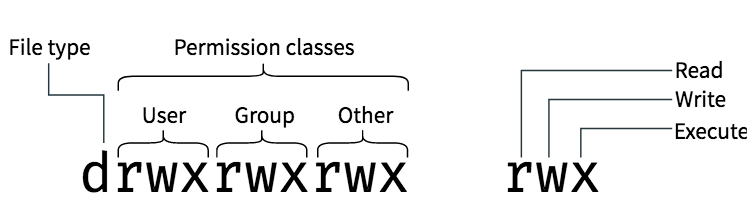
An Introduction To Linux File Permissions Boolean World

Go File Permissions On Linux Wenzr
Chmod Github Topics Github

Workbook 4 File Ownerships And Permissions Ppt Video Online Download

Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks

30 Best Aio Linux Workshop Images Linux Workshop Email Server

Linux Chmod Calculator Chmodcalculator

Chmodcalculator

Pin By Dr Stefan Gruenwald On Cheatsheets Computer Science Programming Learn Javascript Linux Operating System
Your Own Linux Chmod Basics Of Files Directories Permissions And Use Of Chmod

What S An Uppercase T At The End Of Unix Permissions Ask Ubuntu

Linux Admin 101 File Permissions With Chmod Chgrp And Chown Trash Computer
Linux Command Cheat Sheet
An Introduction To Linux File Permissions Boolean World

Unix Linux Permissions Calculator 1 0 Free Download

Understanding File Permissions And Using Them To Secure Your Site

Your Own Linux Chmod Basics Of Files Directories Permissions And Use Of Chmod

Change File Permissions Easily With Online Chmod Calculator Convert

Changing File Permissions During And After Update Web Site Scripts Com
File Permissions In Linux Unix With Example
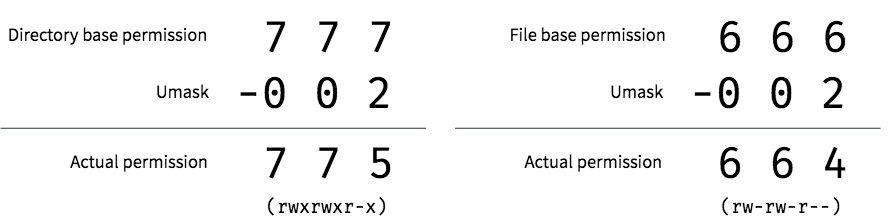
An Introduction To Linux File Permissions Boolean World

Linux Admin 101 File Permissions With Chmod Chgrp And Chown Trash Computer

Workbook 4 File Ownerships And Permissions Ppt Video Online Download

0xax Reading Writing Cheat Sheets Cheating
Your Own Linux Chmod Basics Of Files Directories Permissions And Use Of Chmod

Posted Withrepost Terminalworld It Is The First Column In The Output Of Ls L Command Which Tells All About The Linux Linux Permissions Software Engineer

19b Permissions
Umask Calculator Calculate A Umask Value In Linux Permissions



